
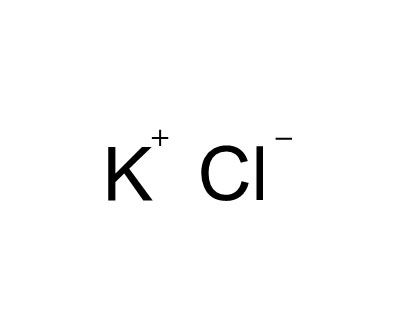
Potassium chloride(Chemical formula: KCl), English: Potassium chloride. A type of hydrochloride salt, white crystalline or crystalline powder, easily soluble in water and glycerol, insoluble in alcohols, insoluble in ethers and acetone.
| Chinese name | 氯化钾 | English name | Potassium chloride |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese alias | English alias | Sylvite;Muriate of potash; | |
| CAS | 7447-40-7 | Molecular formula | ClK |
| Molecular weight | 74.55130 | Accurate mass | 73.93260 |
| PSA | 0.00000 | LOGP | -2.99600 |
| UNII | 660YQ98I10 |
|---|
Appearance and characteristics:
White crystal
Density:
1.98 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
Boiling point:
1420°C
Melting point:
770 °C(lit.)
Flash point:
1500°C
Refractive index:
n20/D 1.334
Water solubility:
340 g/L (20 ºC)
Stability:
Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids. Protect from moisture. Hygroscopic.
Storage conditions:
2-8ºC
RTECS:
TS8050000
Safety instructions:
S24/25-S39-S26-S22-S23
WGK Germany:
one
Hazard category code:
R36
Customs code:
three billion one hundred and four million two hundred and nine thousand
Hazard category:
five point one
Packaging grade:
II
Dangerous goods signs:
Xi
1. The recrystallization method involves adding industrial potassium chloride to a dissolution tank containing distilled water for dissolution, followed by the addition of decolorizing agents, arsenic removal agents, and heavy metal removal agents for solution purification. After precipitation, filtration, cooling crystallization, solid-liquid separation, and drying, edible potassium chloride products are obtained.
2. Carnolite, a rock salt mainly composed of magnesium chloride and potassium chloride, is crushed, mixed with 75% water, passed through superheated steam, and cooled to precipitate potassium chloride. This crude crystal is obtained by washing with water and refining through recrystallization. The mother liquor obtained by precipitating sodium chloride from seawater is concentrated, crystallized, and refined.
3. The flotation method first crushes and grinds potassium salt ore (or sand crystal salt) in a ball mill, then adds 1% octadecylamine flotation agent while stirring, and at the same time adds 2% cellulose for flotation. After centrifugal separation, potassium chloride products are obtained. The decomposition flotation combined method first screens the carnallite, and then crushes the crude product. Water, mother liquor, and flotation agent are added for decomposition, followed by coarse selection, selection, filtration, washing, centrifugal separation, and drying to produce potassium chloride finished product. The brine mixing method first mixes bitter brine with old brine (thick brine) in a certain proportion, allows it to stand, and after the bitter brine is analyzed, the mixed brine is obtained. Then, the mixed brine is evaporated and concentrated, and placed in a thermal insulation settler to allow the high and low temperature salt to settle and obtain a clear liquid. After cooling, crystallization, and centrifugal separation, carnallite is obtained. Decompose carnallite with water to obtain crude potassium chloride, which is then separated by centrifugation, washed with water, separated by centrifugation, and dried to obtain the finished potassium chloride product.
4. The brine mixing method mixes the bitter brine and old brine (mother liquor after precipitation of potassium magnesium chloride complex salt) from seawater in a certain proportion, so that the molar ratio of magnesium sulfate and magnesium chloride in the mixed brine is below 0.11, and the ratio of magnesium chloride to potassium chloride is around 11. The bitter salt (containing 90% sodium chloride, 2% magnesium chloride, 1% magnesium sulfate, and 0.4% potassium chloride) is fully precipitated and removed in the brine mixing tank. After evaporating and concentrating the mixed brine to 128 ℃, it is placed in an insulation settler. High temperature salts (containing 40% sodium chloride, 14% magnesium chloride, 13% magnesium sulfate, and 1% potassium chloride) are precipitated at 124 ℃, while low-temperature salts (containing 20% sodium chloride, 17% chloride, 22% magnesium sulfate, and 1.3% potassium chloride) are precipitated at 85-90 ℃. After separation, the filtrate is cooled to precipitate potassium magnesium chloride double salt, which is artificial carnallite. The mother liquor after separating carnallite is old brine. Carnallite is decomposed by adding water to dissolve magnesium chloride, resulting in crude potassium chloride; The latter is washed with water and recrystallized to obtain the finished product. As potassium chloride used in medicine or food, the above product needs to be dissolved in water, filtered, and then saturated with chlorine gas. Boil to remove excess chlorine, then introduce hydrogen chloride to precipitate potassium chloride. After separation, wash with water and dissolve in water, filter and cool to around -5 ℃ to obtain crystals, and dry at 100-120 ℃ to obtain the finished product. The main component of carnallite flotation method is potassium chloride. Potassium chloride is obtained by rough selection and selective selection using water and flotation agents. This product is refined by washing with water and recrystallization to obtain a finished product.
5. Neutralize potassium hydroxide with hydrochloric acid. Add a stoichiometric amount of pure hydrochloric acid to a pure potassium hydroxide aqueous solution, with a slight excess of acid to make the solution slightly acidic. Heat and concentrate the solution, but it still needs to be acidic. After cooling, a precipitate of potassium chloride will precipitate. Filter and place the precipitate in an evaporating dish on a sand bath while stirring and heating to dry. The impurities contained in commercially available potassium chloride are mainly sodium chloride and magnesium chloride, as well as small amounts of sulfates, iron salts, aluminum salts, etc. Take 500g of commercially available potassium chloride and 1.5L of distilled water, grind them together, filter them, and place the filtrate in an evaporating dish. Add 5g of lime milk made from 5g of calcium oxide and 12g of pure barium chloride, stir thoroughly, and take a small amount of upper clear liquid after precipitation. Add barium chloride dropwise to confirm that no precipitation has been formed. Filter and add 15g of pure anhydrous potassium carbonate to the filtrate. Stir and let it stand. Filter and heat the filtrate to boiling. Add dilute hydrochloric acid to make it acidic. Concentrate by direct fire until the volume is concentrated to 1/3, and potassium chloride will precipitate. After cooling, filter the crystals by suction, place them in an evaporating dish, and dry them in a sand bath.
6. Add 25 parts of distilled water to 10 parts of industrial potassium chloride, heat and stir evenly, introduce hydrogen sulfide gas or hydrogen sulfide solution into the solution to completely precipitate heavy metal sulfides, then add a small amount of activated carbon and a small amount of hydrogen peroxide, and then add an appropriate amount of saturated barium chloride solution, and check whether SO42- ions precipitate completely. Filter the solution and heat it for 5 minutes. Add potassium carbonate to bring the pH of the solution to 11-12, and check if Ba2+ions have completely precipitated (acidify the filtrate sample with dilute sulfuric acid, and if the solution remains turbid or does not precipitate, it is considered qualified). Filter while hot, neutralize the filtrate with chemically pure hydrochloric acid to pH=7, stir evenly, and allow the filtrate to cool and crystallize. Crystalline spin drying, at (100)
Dry at ± 5 ℃ before packaging. The amount of barium chloride and potassium carbonate added during the process should be determined based on the content of SO42 and Ca2+ions in the raw material potassium chloride (industrial product). If mechanical stirring (150-200 revolutions per minute) is used during crystallization, the purity of the obtained reagent will be much higher (in terms of the content of sulfate impurities and ammonium impurities).
7. The cold decomposition method crushes the carnallite and places it into a decomposer. Water, mother liquor, and flotation agent are added for decomposition, and the crude potassium slurry discharged from the lower part of the decomposer is pumped into the settling device. The settling slurry is discharged from the bottom of the reactor, and after centrifugal separation, crude potassium is obtained by removing the mother liquor. The crude potassium is sent into the scrubber, and the sodium chloride contained in it is dissolved in water at room temperature. The slurry is then further settled, centrifuged, and dried to obtain the finished potassium chloride product. Clear liquid is used as the mother liquor of refined potassium and recycled.
Used for the production of other potassium salts, as well as in medicine, metal heat treatment, photography, and the production of magnesium metal. It is also used as an electrolyte supplement, a nutritional supplement, a gelling agent, a salt substitute, and yeast feed for the treatment of hypokalemia.